Training courses
The Bologna process

(this page is currently under translation – current displayed text is an automated rough translation – thank for your understanding)
The Bologna Process , initiated in 1998, is a process of bringing together European higher education systems. In 2010, it resulted in the creation of the EHEA , European Higher Education Area , which can be translated as the European Higher Education Area .
This international collaboration involves 49 states, including the countries of the European Union, Turkey, Russia, etc., jointly committed to structural reforms of their educational system, the sharing of tools and knowledge. Together, they agree to adopt these reforms of their higher education based on common values: freedom of expression, autonomy of institutions, independence of student unions, free movement of students and teaching staff, etc. For example, stakeholders are constantly adapting their higher education, strengthening equivalences and compatibilities from one country to another, and optimizing program quality guarantees.
The objective of the EHEA is to promote European knowledge on a global scale, but also to promote student mobility and offer them better employability .
For more information, please go to the EHEA official website
Among the projects and tools that have been developed jointly by the various EHEA stakeholders, we can note the structuring of the training in three cycles and the implementation of the ECTS (European credits transfer system) credit system.
Structuring the European academic system : the 3 cycles
| 1st cycle | 2nd cycle | 3rd cycle | |
| Bachelor | Master | Doctorate | |
|
Licence (or DNL – diplôme national de licence) |
Master (or DNM – diplôme national de master) |
Doctorat (or DND – diplôme national de doctorat) |
|
| Years |
L1 – L2 – L3 (3 years) |
M1 – M2 (2 years) |
D1 – D2 – D3 (3 years) |
This breakdown is also known as the LMD System (Licence-Master-Doctorate).
The E.C.T.S. system (European credits transfer system)
ECTS is a European grading scale system. A harmonized EHEA tool, it works by accumulating and transferring credits, known as ECTS credits. Each successful trimester validates 30 ECTS. Intended to make studies and courses more transparent, it also helps students to move around during their training course while allowing them to have their university qualifications recognized from one country to another. The flexibility it offers in the composition of each student’s training course is one of its major assets.
Each lesson followed by the student includes a knowledge test, with a mark ranging from 0 (min) to 20 (max). A minimum general average of 10/20 is necessary to validate the semester or the year of training.
To find out more about the ECTS credit system:
A user guide is available on the European Commission website
“Domaines-Mentions-Parcours” and “Spécificités-Options”
The Order of January 22, 2014 setting the national framework for training leading to the award of national bachelor ‘s, professional license and master ‘s degrees , as well as the Order of July 30, 2018 which modifies it, stipulated that for each cycle of higher education, establishments had to structure their training offer in areas , specializations and training paths (Art.1, Art 7.).
The main aim is to make this training offer more readable. National diplomas are therefore now defined by a domain name and mention, and if necessary a name of a training course.
The area that robotics is interested in is Science , Technology and Health.
The Commission of Engineering Titles (CTI), following deliberation n° 2017/01-03 relating to the nomenclature of engineering title specialties, classifies engineering schools into specialties and options.
The titles of fields and mentions are validated within the framework of the national procedure of accreditation by the minister in charge of higher education, after opinion of the National council of higher education and research. Then, within the fields and specializations, the establishments organize under their responsibility the different training courses and set their names.
Thus, if we are particularly interested in the fields and mentions of your future training course in robotics:
| Licence Professionnelle | Licence | Master | ENGINEERING SCHOOL |
|
Mentions : . Industry Professions: Mechatronics, Robotics . Industry Professions: Industrial Production Management . Maintenance and Technology: industrial control. Maintenance and technology: multi-technical systems . Maintenance of industrial, production and energy systems . Industry jobs: industrial logistics . Industry professions: design and improvement of industrial processes and procedures . Automated systems, networks and industrial computing |
Mentions : . Mechanical . Electronics, electrical energy, automatic . science and technology . Sciences for the engineer . Computer science |
Mentions : . Automatique, Robotique . Electronique, Energie électrique, Automatique . Ingénierie des Systèmes Complexes . Génie Industriel . Sciences pour l’ingénieur . Ingénierie de conception . Mécanique . Génie mécanique . Ingénierie nucléaire . Informatique |
Spécialités : . Informatique . Informatique industrielle . Mécatronique . Systèmes numériques . Robotique . Logistique . Systèmes () embarqués
|
| Course : Courses specific to each establishment |
Options : Courses specific to each establishment |
||
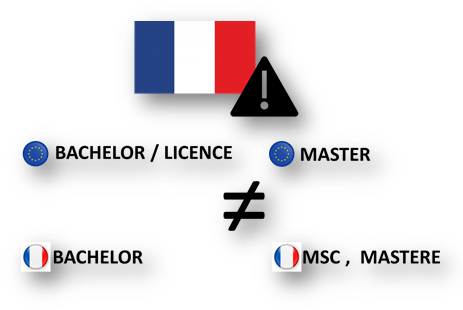
Pay attention to the terminology
In France, the “bachelor”, the “master of science” or even the “mastère” are not to be confused with the “bachelor” and the “master” of the English language
Indeed, the bachelor ‘s degree , the master of science and the master ‘s degree in France are diplomas from establishments which can be issued outside the university system (by business schools, IEP, or other private establishments), at Bac + 3 (for the bachelor), bac+5 (for the master of science ) or bac+6 (for the specialized master ).
Unlike the license or the master of the harmonized LMD system, they are not automatically recognized as national diplomas by the Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Innovation.
The bachelor, the master of science, the master do not necessarily offer the same guarantees and the same equivalences as the diplomas of the LMD system. This does not mean that these courses are less good , they can also relate to specific sectors and be well recognized by professionals in these sectors. It is up to everyone to check this point by building their professional career!
About twenty European masters are, for example, offered by the European Federation of Schools (FEDE), with European recognition and 500 partner establishments throughout Europe. Their diplomas are recognized by the professionals concerned by the content of these training courses, but not by the State. Since 2020 and for some establishments, the bachelor can issue a diploma giving right to the grade of L2 or L3. Finally, we can also cite by way of illustration the Conférence des Grandes Ecoles (CGE), an independent body which issues recognition to highly demanding bac+5 or bac+6 training, in all sectors. To carry this protected label, the training must be validated by the Conference of Grandes Ecoles.
To find out more, you can peruse the following government decisions (in French) :
as well as :
mentions de licences et masters